The Drake Passage is one of the most significant and challenging bodies of water in the world. It serves as the key maritime route connecting the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans, sitting between the southern tip of South America and Antarctica. This passage is not only notable for its geographical importance but also for its notorious reputation due to its unpredictable and often tumultuous weather conditions. As the gateway for expeditions to Antarctica, the Drake Passage holds both scientific and historical significance.
Geography and Location of the Drake Passage
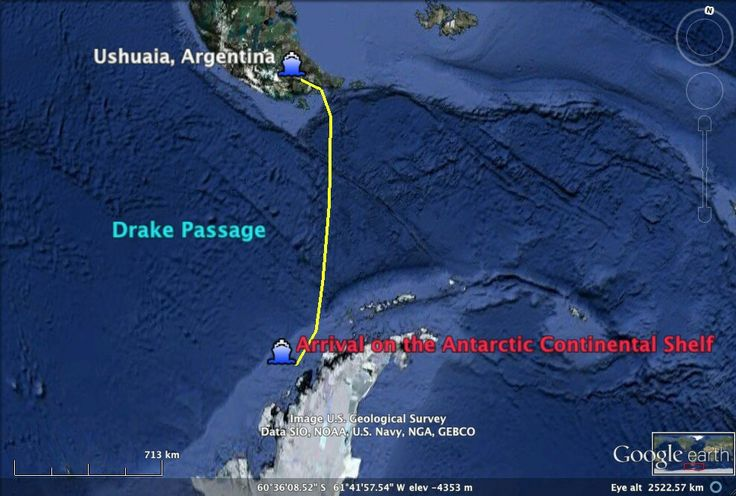
The Drake Passage stretches over approximately 800 kilometers (500 miles) from the southern tip of South America at Cape Horn to the Antarctic Peninsula. It is named after the English explorer Sir Francis Drake, who navigated the waters in the late 16th century. The passage lies at a unique crossroads between the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans, connecting them with the Southern Ocean.
The northernmost point of the Drake Passage is bordered by the Beagle Channel, while the southern boundary lies near the Antarctic Peninsula. The passage serves as the only natural route from the South American continent to the frozen lands of Antarctica, making it essential for scientific research and exploration.
The Role of the Drake Passage in Antarctic Exploration
The Drake Passage holds immense historical and scientific significance. It has been the route taken by many of the early explorers who sought to discover Antarctica and its resources. One of the most famous explorers to navigate the Drake Passage was Sir Ernest Shackleton, whose Imperial Trans-Antarctic Expedition of 1914-1917 aimed to cross the continent from coast to coast. Although Shackleton’s mission was ultimately thwarted by a series of unforeseen events, the expedition is remembered for its incredible survival story, much of which unfolded after the ship, the Endurance, became trapped in the ice of the Weddell Sea.
In modern times, the Drake Passage remains vital for research expeditions and travel to Antarctica. Cruise ships, research vessels, and private yachts use the passage as a route for scientific exploration, tourism, and resupply missions. Antarctica, being one of the most pristine and uninhabited places on Earth, requires a careful and considered approach to exploration, and the Drake Passage provides the only viable access point from the South American continent.
The Harsh Conditions of the Drake Passage
Known for its unpredictable and often violent weather patterns, the Drake Passage is one of the most notoriously challenging stretches of ocean for mariners. The passage is situated at the convergence of several major ocean currents, including the Antarctic Circumpolar Current (ACC), which circles the Southern Ocean and flows uninterrupted around Antarctica. The convergence of these currents, along with the passage’s location between two major oceans, creates conditions that can make navigation a difficult and sometimes dangerous undertaking.
Wind and Storms
The winds in the Drake Passage are incredibly strong and can reach hurricane-force speeds, especially during the austral summer months when the region experiences the least amount of daylight. The winds primarily blow from the west and can whip up large, dangerous waves that make travel treacherous. The powerful winds and rapidly changing weather patterns are a hallmark of the passage, earning it the moniker “the wildest sea in the world.”
Waves and Swells
Due to the unique geography of the Drake Passage, waves can become towering and unpredictable. The shallow depth of the passage combined with the powerful winds leads to the development of massive swells, some of which can reach heights of up to 15 meters (49 feet). This can make the passage incredibly hazardous for vessels, especially smaller boats that are not equipped to handle such conditions. Even larger vessels are known to experience significant motion, making the journey uncomfortable and disorienting for passengers and crew alike.
Ice and Icebergs
Icebergs are another major challenge for those navigating the Drake Passage. While the passage itself is free of permanent ice, the surrounding waters are filled with icebergs and sea ice, particularly in the winter months. Ships must navigate carefully to avoid these massive, floating blocks of ice, which can be a serious threat to navigation. The presence of these icebergs marks the proximity of Antarctica, and travelers heading toward the continent must be vigilant when entering the region.
The Drake Passage as a Hub for Marine Life
Despite its harsh conditions, the Drake Passage is home to a variety of unique and fascinating marine life. The cold waters of the Southern Ocean, combined with the nutrient-rich upwellings that occur in the passage, provide an ideal environment for marine ecosystems to thrive.
Whale Watching
One of the most popular activities for tourists passing through the Drake Passage is whale watching. The passage is a prime location for observing various species of whales, including humpback whales, orcas, and blue whales. These whales migrate through the region in search of food, particularly krill, which is abundant in the nutrient-rich waters. The presence of these majestic creatures has made the Drake Passage a prime location for researchers and nature enthusiasts alike.
Birdlife
The passage is also a haven for seabirds, including species such as albatrosses, petrels, and shearwaters. These birds are highly adapted to life in the southern seas and can often be seen gliding gracefully over the waves. The wandering albatross, known for its incredible wingspan of up to 3.5 meters (11 feet), is one of the most iconic birds found in the region. Birdwatching in the Drake Passage offers an exciting opportunity to observe some of the most impressive and specialized birds on the planet.
Marine Mammals and Fish
In addition to whales and seabirds, the Drake Passage is home to seals, such as the Weddell seal, leopard seals, and crabeater seals. These animals can be seen lounging on ice floes or swimming in the frigid waters of the passage. The waters also support an array of fish species, including Antarctic toothfish and icefish, which have adapted to survive in the extreme cold.
The Importance of the Drake Passage for Climate Science
The Drake Passage plays a critical role in the study of global climate systems. As the Southern Ocean is one of the Earth’s largest carbon sinks, the waters surrounding Antarctica have a significant impact on the planet’s climate. Scientists study the region to understand how ocean currents, wind patterns, and the movement of water masses influence global climate and weather patterns.
Researchers also use the passage to monitor changes in ice cover, as the melting of Antarctic glaciers has a direct impact on sea levels. The Drake Passage provides a gateway for scientists to access one of the most important regions in the study of climate change.
Tourism and Expeditions through the Drake Passage
The Drake Passage has become a popular route for tourists seeking to visit Antarctica. Expedition cruises often depart from Ushuaia, Argentina, and cross the passage to reach the Antarctic Peninsula. The journey typically takes two to three days, during which passengers can experience the wild seas and unique wildlife of the Southern Ocean.
While the conditions in the passage can be challenging, modern ships are well-equipped to handle the rough waters. Many expedition cruises also offer educational programs to teach passengers about the importance of Antarctica and the environment, as well as the history of the region.
For travelers, the Drake Passage represents an adventure in itself. The journey is a testament to human endurance and exploration, as passengers are taken through one of the most remote and untamed parts of the world.
Conclusion:
The Drake Passage is more than just a body of water connecting two continents; it is a symbol of the challenges and wonders of the natural world. Its unpredictable weather, massive swells, and icy waters make it a formidable obstacle for mariners, but it also provides a gateway to one of the most pristine and mysterious places on Earth—Antarctica. From its role in historical exploration to its significance in modern scientific research and tourism, the Drake Passage remains a vital and captivating part of the planet’s geography. Whether you’re a scientist, a sailor, or a traveler, crossing the Drake Passage is an unforgettable experience, marking a journey into the unknown that few can fully comprehend.























